What Leads To Heel Pain And How To End It
Overview
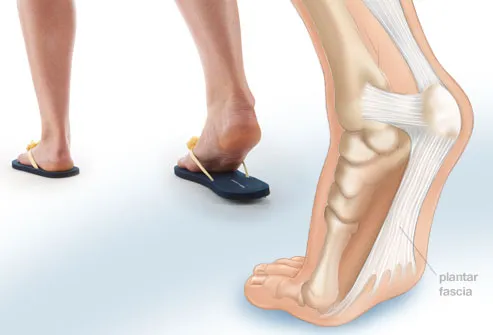
The Plantar Fascia is a strong ligament-like structure under the arch of the foot that runs from the heel bone to the ball of the foot. If we could see it in isolation it has a triangular shape when looked at from underneath but has a curved shape when looked at from the side - much like a sail boat’s sail billowing in the wind. The most functional piece is from the front-bottom-inside area of the heel bone (calcaneous) to the joint of the big toe (hallux) and this is where the majority of stress of walking (and running and jumping) is taken by the fascia. How your plantar fascia reacts to and recovers from this stress is what determines the extent and nature of your plantar fasciitis.
Causes
Factors which may contribute to plantar fasciitis and heel spurs include a sudden increase in daily activities, increase in weight (not usually a problem with runners), or a change of shoes. Dramatic increase in training intensity or duration may cause plantar fasciitis. Shoes that are too flexible in the middle of the arch or shoes that bend before the toe joints will cause an increase in tension in the plantar fascia. Even though you may have run in shoes that are flexible before, now that you have developed plantar fasciitis, make certain that your shoe is stable and does not bend in the midfoot. Check and be certain that your shoes are not excessively worn. Shoes that do not sufficiently control excessive pronation combined with an increase in training can lead to this condition. A change in running style or parameters, such as starting speed work, running on the ball of your foot or sudden increase in hill workouts may lead to problems. All changes should be gradual and not abrupt. Gait changes such as altering your foot strike, switching shoe style, running barefoot or in minimalist shoes should all be made gradually and not abruptly. The "terrible too's" of too much, too soon, too often with too little rest also applies to "too many changes with too little adaptation". Make your changes gradually and allow your muscles, bones, and other body structures to adapt to the alterations you may be attempting.
Symptoms
The main symptom of plantar fasciitis is heel pain when you walk. You may also feel pain when you stand and possibly even when you are resting. This pain typically occurs first thing in the morning after you get out of bed, when your foot is placed flat on the floor. The pain occurs because you are stretching the plantar fascia. The pain usually lessens with more walking, but you may have it again after periods of rest. You may feel no pain when you are sleeping because the position of your feet during rest allows the fascia to shorten and relax.
Diagnosis
Most cases of plantar fasciitis are diagnosed by a health care provider who listens carefully to your description of symptoms. During an examination of your feet, your health care provider will have to press on the bottom of your feet, the area most likely to be painful in plantar fasciitis. Because the pain of plantar fasciitis has unique characteristics, pain upon rising, improvement after walking for several minutes, pain produced by pressure applied in a specific location on your foot but not with pressure in other areas, your health care provider will probably feel comfortable making the diagnosis based on your symptoms and a physical examination. Your health care provider may suggest that you have an X-ray of your foot to verify that there is no stress fracture causing your pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Heel cups are used to decrease the impact on the calcaneus and to theoretically decrease the tension on the plantar fascia by elevating the heel on a soft cushion. Although heel cups have been found to be useful by some physicians and patients, in our experience they are more useful in treating patients with fat pad syndrome and heel bruises than patients with plantar fasciitis. In a survey of 411 patients with plantar fasciitis, heel cups were ranked as the least effective of 11 different treatments.
Surgical Treatment
If you consider surgery, your original diagnosis should be confirmed by the surgeon first. In addition, supporting diagnostic evidence (such as nerve-conduction studies) should be gathered to rule out nerve entrapment, particularly of the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve and the medial plantar nerve. Blood tests should consist of an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), rheumatoid factor, human leukocyte antigen B27 (HLA-B27), and uric acid. It’s important to understand that surgical treatment of bone spurs rarely improves plantar fasciitis pain. And surgery for plantar fasciitis can cause secondary complications-a troubling condition known as lateral column syndrome.